[ Skywatchers ] [ Main Menu ]
47119
From: ryan, [DNS_Address]
Subject: Asteroid coming exceedingly close to Earth, but will miss
URL: https://www.sfgate.com/news/article/asteroid-coming-exceedingly-close-to-earth-but-17742138.php
|
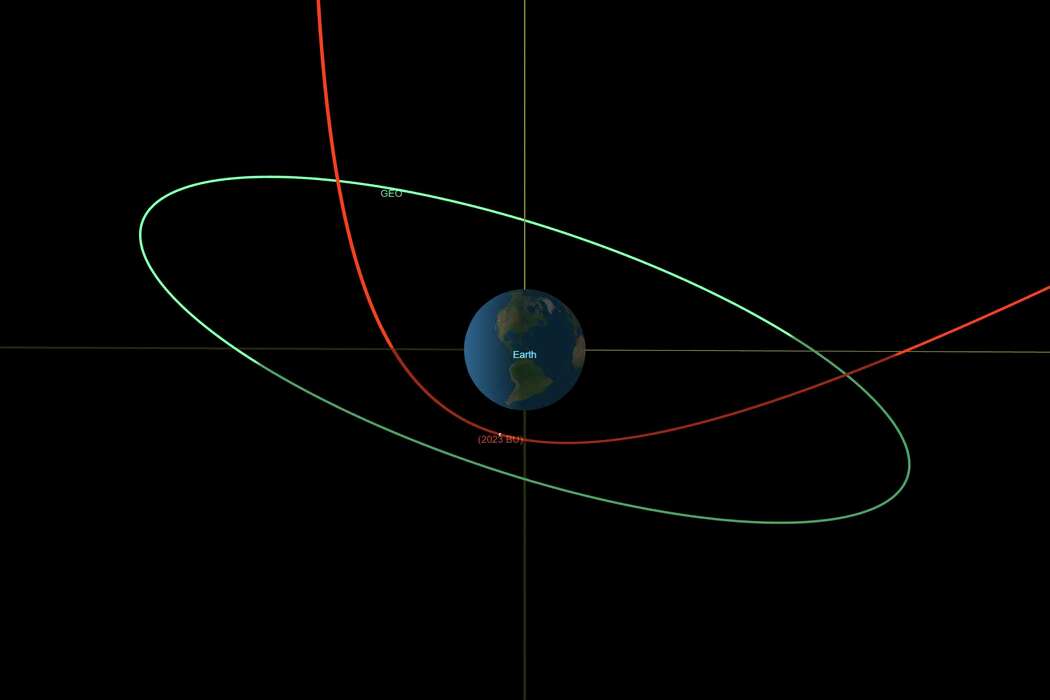
Asteroid coming exceedingly close to Earth, but will miss MARCIA DUNN, AP Aerospace Writer Jan. 25, 2023 This diagram made available by NASA shows the estimated trajectory of asteroid 2023 BU, in red, affected by the earth's gravity, and the orbit of geosynchronous satellites, in green. On Wednesday, Jan. 25, 2023, NASA revealed that this newly discovered asteroid, about the size of a truck, will zoom 2,200 miles above the southern tip of South America Thursday evening. Scientists say there is no risk of an impact. Even if it came a lot closer, scientists say it would burn up in the atmosphere, with only a few small pieces reaching the surface. (NASA/JPL-Caltech) CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. (AP) — An asteroid the size of a delivery truck will whip past Earth on Thursday night, one of the closest such encounters ever recorded. NASA insists it will be a near miss with no chance of the asteroid hitting Earth. NASA said Wednesday that this newly discovered asteroid will zoom 2,200 miles (3,600 kilometers) above the southern tip of South America. That's 10 times closer than the bevy of communication satellites circling overhead. The closest approach will occur at 7:27 p.m. EST (9:27 p.m. local.) Even if the space rock came a lot closer, scientists said most of it would burn up in the atmosphere, with some of the bigger pieces possibly falling as meteorites. NASA's impact hazard assessment system, called Scout, quickly ruled out a strike, said its developer, Davide Farnocchia, an engineer at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. "But despite the very few observations, it was nonetheless able to predict that the asteroid would make an extraordinarily close approach with Earth,” Farnocchia said in a statement. “In fact, this is one of the closest approaches by a known near-Earth object ever recorded.” Discovered Saturday, the asteroid known as 2023 BU is believed to be between 11 feet (3.5 meters) and 28 feet (8.5 meters) feet across. It was first spotted by the same amateur astronomer in Crimea, Gennady Borisov, who discovered an interstellar comet in 2019. Within a few days, dozens of observations were made by astronomers around the world, allowing them to refine the asteroid's orbit. The asteroid's path drastically will be altered by Earth's gravity once it zips by. Instead of circling the sun every 359 days, it will move into an oval orbit lasting 425 days, according to NASA. |
47143

From: ryan, [DNS_Address]
Subject: Re: Asteroid coming exceedingly close to Earth, but will miss
URL: https://www.sfgate.com/news/article/green-comet-watching-bay-area-17741696.php
|
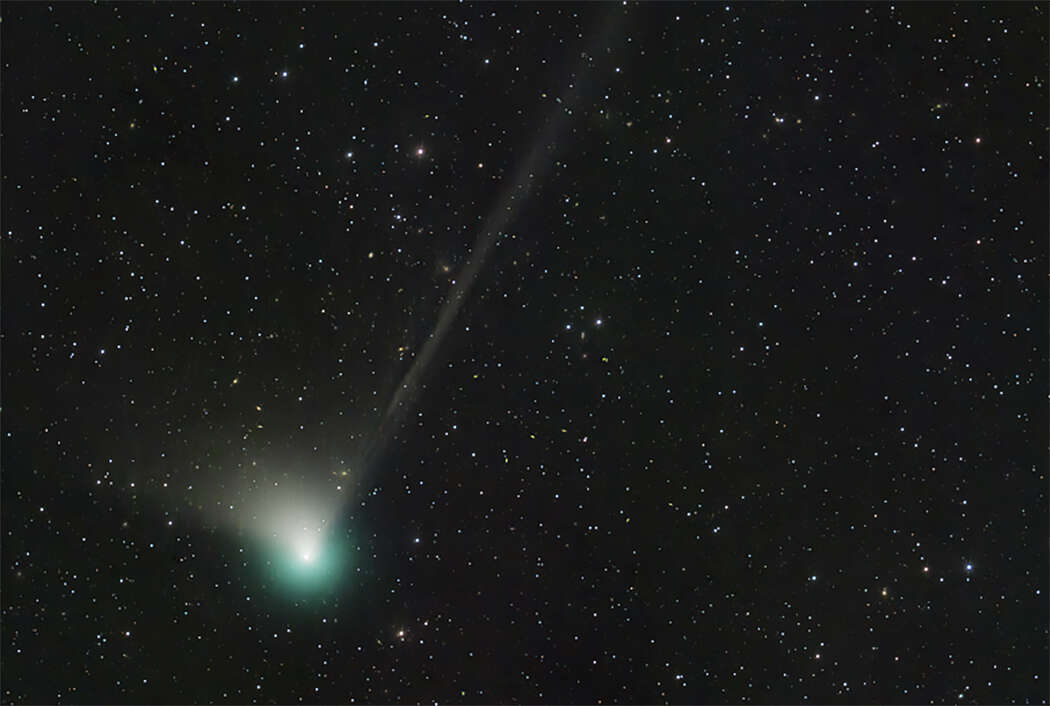
'It may never come back': Rare green comet flies over Bay Area Amanda Bartlett, SFGATE Jan. 26, 2023 Comet C/2022 E3 (ZTF) was discovered by astronomers using the wide-field survey camera at the Zwicky Transient Facility in early March 2022. Comet C/2022 E3 (ZTF) was discovered by astronomers using the wide-field survey camera at the Zwicky Transient Facility in early March 2022. Image via NASA A rare green comet is passing through our solar system for the first time in 50,000 years, and over the weekend, Bay Area stargazers could have the best chance of spotting it in the night sky. Dubbed C/2022 E3 (ZTF), the comet was first discovered in Jupiter’s orbit last March by astronomers Frank Masci and Bryce Bolin at the Palomar Observatory in San Diego County, and named after the Zwicky Transient Facility where it was identified. The comet made its closest approach to the sun on Jan. 12, and is now on a path that will bring it closest to Earth — about 27 million miles away — on Feb. 2. Paul Lynam, an astronomer at the Lick Observatory on Mount Hamilton, told SFGATE it’s unlikely that anyone in the Bay Area will be able to see the comet with the naked eye due to light pollution, so a backyard telescope — or ideally, a small pair of binoculars, which offer a wider field of view — will come in handy. Lynam witnessed the comet from the observatory at about 9 p.m. on Wednesday night, and recommends that people look for it by scanning the northeastern night sky between the Big Dipper and the Little Dipper. “What I noticed with a cheap pair of binoculars was an extended, diffused object that was more spread out than a star, and slightly brighter,” he said. “It looked like a lady’s hand fan that was open at an angle slightly less than 90 degrees.” If you can’t see it right away, don’t give up. “Comets have already been known to change their appearance quite quickly from night to night,” Lynam said. “If you are able to see it, you may recognize that it’s moving relative to the stars in the background, and if you’re lucky, you may see the morphology — the shape and structure of the tail.” Gerald McKeegan, an astronomer at the Chabot Space & Science Center in Oakland, said the comet may even appear to have two tails — one made of gas and one made of particles. He believes there’s still a chance observers “in very dark sky locations far from city lights” might be able to see it without visual aids from now until the first few days of February. After that, the comet will remain in the night sky, but it will become increasingly difficult to see from the U.S. as it moves over the southern hemisphere. Comet C/2022 E3 (ZTF) in the sky of Molfetta, Italy, before sunrise around 6 a.m. on Jan. 24, 2023. It last passed Earth 50,000 years ago, when Neanderthals still lived in our latitudes. The comet was discovered in early March 2022 and was initially thought to be an asteroid. Comet C/2022 E3 (ZTF) in the sky of Molfetta, Italy, before sunrise around 6 a.m. on Jan. 24, 2023. It last passed Earth 50,000 years ago, when Neanderthals still lived in our latitudes. The comet was discovered in early March 2022 and was initially thought to be an asteroid. NurPhoto via Getty Images The comet gets its namesake shade of green from carbon-based compounds that interact with ultraviolet light in the atmosphere, which then break down and produce dicarbon, a molecule that emits the color. However, observers shouldn’t expect the comet to zoom across the sky in a vibrant, shamrock-colored hue, David Prosper, a night sky network administrator with the Astronomical Society of the Pacific in San Francisco, told SFGATE. “The funny part is while it's called the green comet, the color isn't really noticeable unless you get some good magnification on it,” said Prosper, who is also an administrator of the NASA Night Sky Network. “It seems folks report a definite green color when looking at it through telescopes that are 6 inches in diameter or greater, but everyone's eyes are different. Photos do show the green color readily.” Unfortunately, there are a number of factors at play that could impact the visibility of the comet. Prosper told SFGATE the moon is expected to become increasingly bright over the next week, and Dalton Behringer, a meteorologist with the National Weather Service, said scattered to broken stratus clouds as well as a chance of rain may hinder observers on Saturday and Sunday night. “If people are really trying to see it, they could go into higher terrain and get above the cloud layer,” Behringer said. That being said, Thursday and Friday night could be your best bet. Later this weekend, stargazers may have more luck by heading over to the Chabot Space & Science Center, which plans to host free telescope viewing from 7:30 to 10:30 p.m. on Saturday and Sunday night, and again on Feb. 3 and 4. San Francisco Amateur Astronomers plans to host a public star party this Saturday from 6 to 10 p.m. at the Presidio Parade Grounds. Lynam and McKeegan also suggested looking out for Jupiter, which will appear as one of the brightest lights in the western sky — you can even take a look at the four moons cycling around the planet if you have a pair of binoculars. Mars will also be visible, emitting a bright orange or red light. Regardless of what you might find among the stars, it’s worth taking a look up, as the comet’s orbit is unpredictable and thousands of years could pass before it returns, if it does at all. “We can’t definitively say what the comet’s orbit will be. It could come once and get thrown out of our solar system completely,” Lynam said. “It could take thousands of years, or it may never come back.” |
Responses:
None
47124
From: Eve, [DNS_Address]
Subject: Re: Asteroid coming exceedingly close to Earth, but will miss
|
I am watching this news also. This asteroid is currently in the Lynx constellation fwiw...providing a link for any interested. Cinnamon said once when I shared this link her computer did weird stuff but no one else had issue or said anything ...I visit this link on regular basis no problems. (not showing this for the Moon as it's not accurate but only for the location of the Lynx constellation) 
|
Responses:
None
[ Skywatchers ] [ Main Menu ]